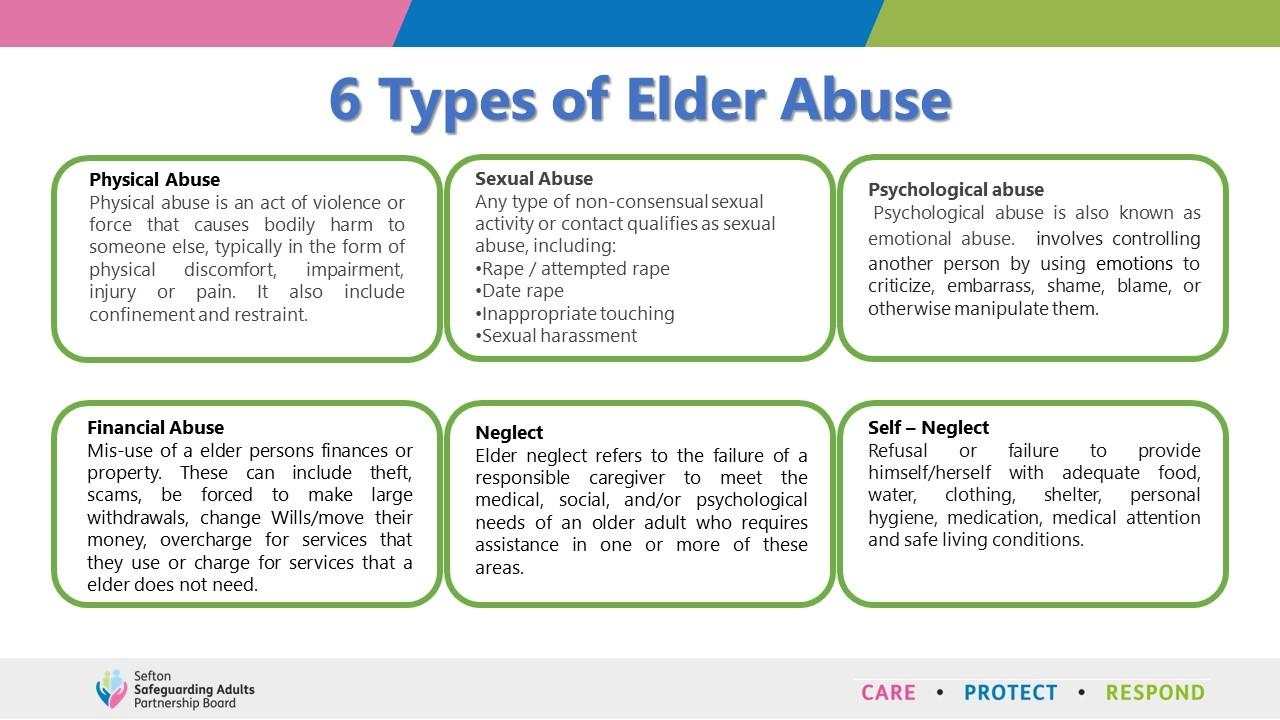
What is Elder Abuse?

World Health Organisation describes Elder abuse can be defined as "a single, or repeated act, or lack of appropriate action, occurring within any relationship where there is an expectation of trust which causes harm or distress to an older person". Elder abuse can take various forms such as financial, physical, psychological and sexual.
The abuse of older people, also known as elder abuse, is an intentional act, or failure to act, by a caregiver or another person in a relationship involving an expectation of trust that causes harm to an adult 60 years and older.
Around 1 in 6 people 60 years and older experienced some form of abuse in community settings during the past year. Rates in institutional settings, such as nursing homes and long-term care facilities, are higher still, with 2 in 3 staff reporting that they have committed abuse in the past year. Even if rates remain constant, the absolute number of older people experiencing abuse is predicted to increase as the global population of older people increases. Abuse of older people can lead to serious physical injuries and long-term psychological consequences, increased risk of nursing home placement, use of emergency services, hospitalization and premature death.
Further Information can be found: